If you’re searching for “Variable Frequency Power Supply,” you might also encounter “Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs).” While they sound similar, they serve two fundamentally different purposes. Using the wrong one can damage your equipment.
This guide will clarify the key differences, helping you choose the perfect solution for your application.
Quick Answer: The Core Difference
- A Variable Frequency Power Supply is designed to provide a clean, stable, and precise AC output with adjustable voltage and frequency. It simulates different power grid conditions for testing electronic devices.
- A Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) is designed to control the speed and torque of a standard AC motor. Its output is not a clean sine wave.
In short: One creates power, the other controls a motor.
Detailed Comparison Table
| Feature | Variable Frequency Power Supply | Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Precise Power Source | Motor Speed Controller |
| Output Waveform | Pure, clean sine wave | Pulse Width Modulated (PWM) wave |
| Design Goal | High stability, low distortion | Cost-effectiveness, motor control |
| Typical Applications | R&D labs, quality assurance, testing devices | Industrial automation, pumps, fans, conveyors |
| Key Benefit | Protects and accurately tests sensitive equipment | Saves energy and extends motor life |
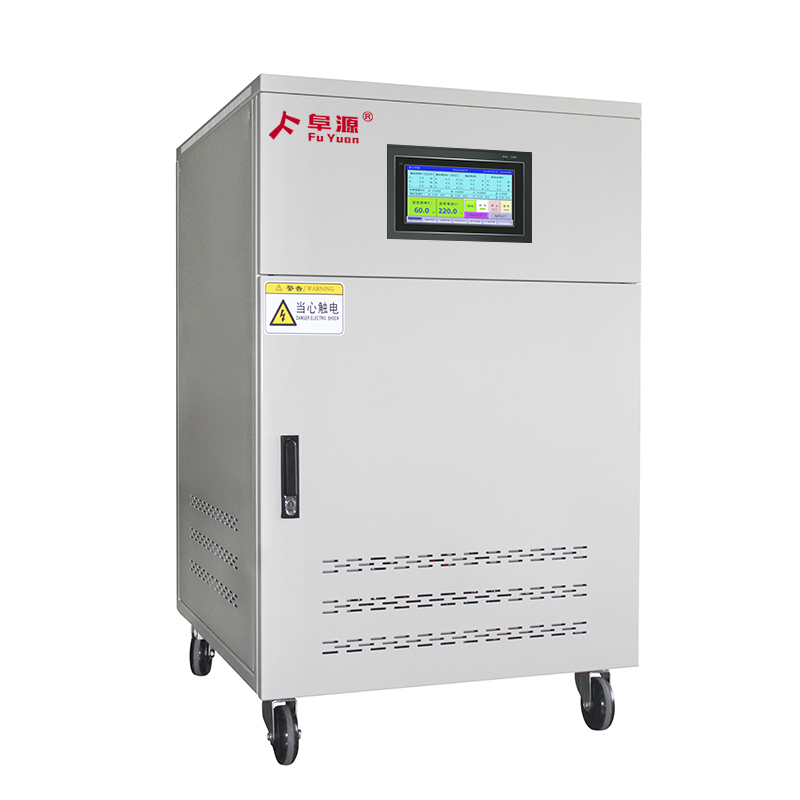
What is a Variable Frequency Power Supply?
A Variable Frequency Power Supply (also known as an AC Power Source) is a sophisticated piece of test equipment. Its main job is to take input power from the wall outlet (e.g., 50Hz, 220V) and deliver a perfectly clean and adjustable AC output (e.g., 0-300V, 45-65Hz to 400Hz).
Why it matters:
Many manufacturers need to test their products under different power conditions—for example, a device destined for the US (60Hz) and Europe (50Hz). A Variable Frequency Power Supply can simulate these conditions perfectly, ensuring the device operates reliably anywhere in the world.
Common Applications:
- Testing and debugging of PCBs and electronic components.
- Quality assurance for appliances, aviation equipment, and military hardware.
- Simulating power sags, surges, and frequency fluctuations.
What is a Variable Frequency Drive (VFD / Inverter)?
A VFD is an industrial control device used to vary the speed and torque of an AC induction motor. It does this by converting the incoming AC power to DC, and then back to a variable-frequency AC using a PWM waveform.
Why it matters:
Running a motor at full speed is often inefficient. A VFD allows you to match the motor’s speed to the required load, leading to significant energy savings and reduced mechanical wear.
Common Applications:
- Controlling conveyor belt speeds.
- Adjusting pump flow and fan blower speeds in HVAC systems.
- Industrial machinery like CNC machines and compressors.
Conclusion: How to Choose
Making the right choice is simple:
- Choose a Variable Frequency Power Supply if you need to…
- Test or power sensitive electronic equipment.
- Simulate various international power grid conditions.
- Conduct R&D or quality validation in a lab environment.
- Choose a Variable Frequency Drive if you need to…
- Control the speed of an AC motor.
- Reduce energy consumption of fans, pumps, or compressors.
- Automate machinery on a factory floor.
For engineers and procurement managers seeking reliable testing solutions, selecting the correct Variable Frequency Power Supply is critical for obtaining accurate and reliable test results. Explore our range of high-precision power supplies to find the perfect fit for your laboratory or production line.